A new tick has been discovered, and its sting makes people allergic to meat
|
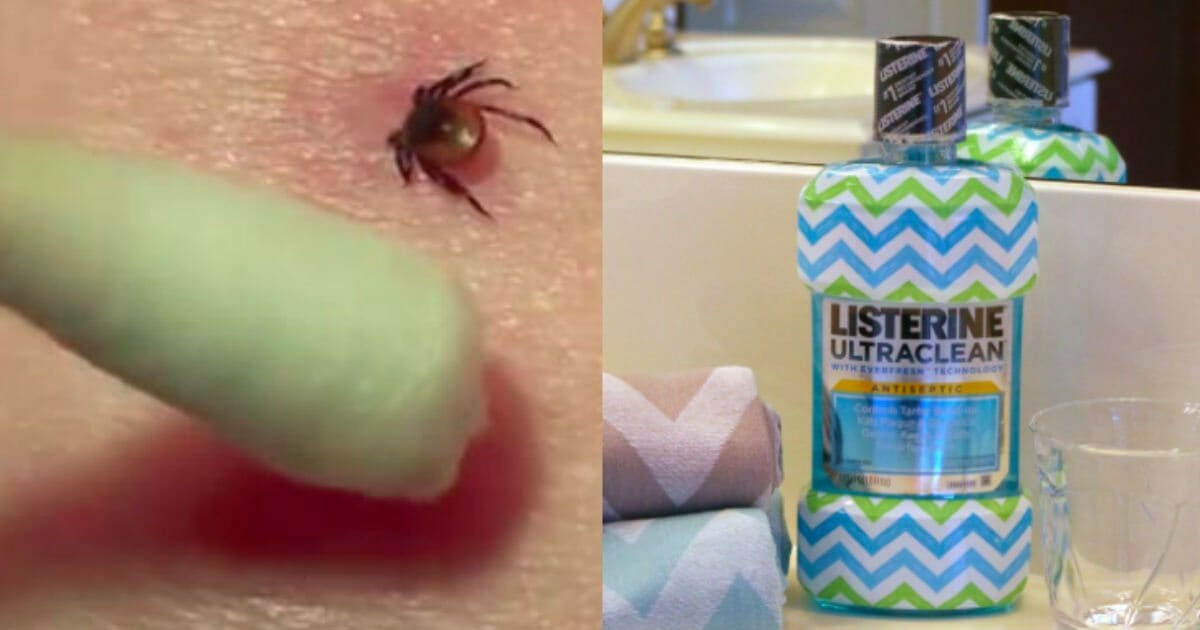
A tick whose sting causes people to become allergic to meat spreads at a dizzying pace.
The "Lone star tick" - which is named after the white mark on its back that resembles Texas - carries a sugar molecule called galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose or alpha-gal, which reprograms the human immune system and makes them allergic to meat permanently.
When a tick with an alpha-gal stings you, the body develops an antibody. Once this happens, whenever you consume a sugar molecule, which is present in red meat, your immune system tries to fight it, causing an allergic reaction.
Symptoms of alpha-gal allergies include urticaria (allergic reaction to the skin), shortness of breath, abdominal pain, and in severe cases severe respiratory difficulty and fainting. In rare cases it can even cause death.
The tick is found mainly in the Southeastern United States, but recently there have also been cases in Minnesota, New Hampshire and other parts of the United States. So its living environment is definitely expanding.
Long Island, New York, reported more than 100 cases last year.
"A warmer climate has caused the tick to reach more northern places", allergist Purvi Parikh told the USA Today.
"Five years ago we had about 50 patients with alpha-gal syndrome, and now there are more than 200..", said Cosby Stone, an expert on immunology and allergies at Vanderbilt University.
Researchers still don't know what is in the saliva of the tick that causes the release of the histamines (the substance that causes the allergic reaction) every time you consume red meat.
The theory includes a bioactive substance similar enough to a alpha-gal molecule that causes a response in the immune system. It may also be a bacteria or a virus, or even a protein residue from the previous feeding of ticks.
The bite of this tick affects all people in the same way, regardless of their genes.
Source: Independent